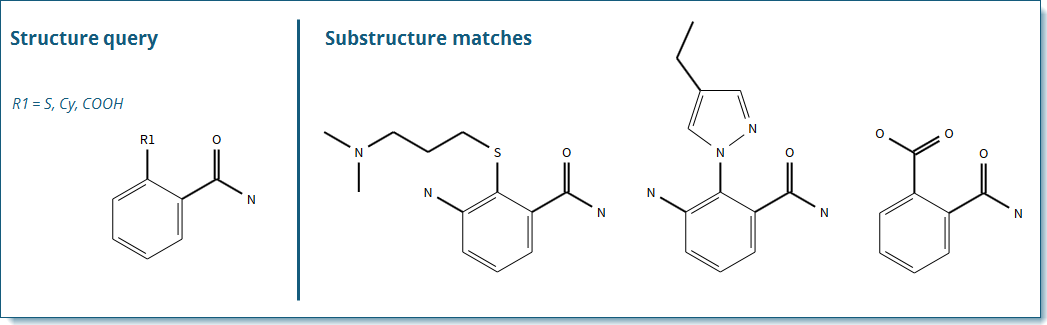
An R-group can contain atoms, variable atoms, shortcuts (functional groups), or fragments.
Note: An attachment point may be added to an R-group node.

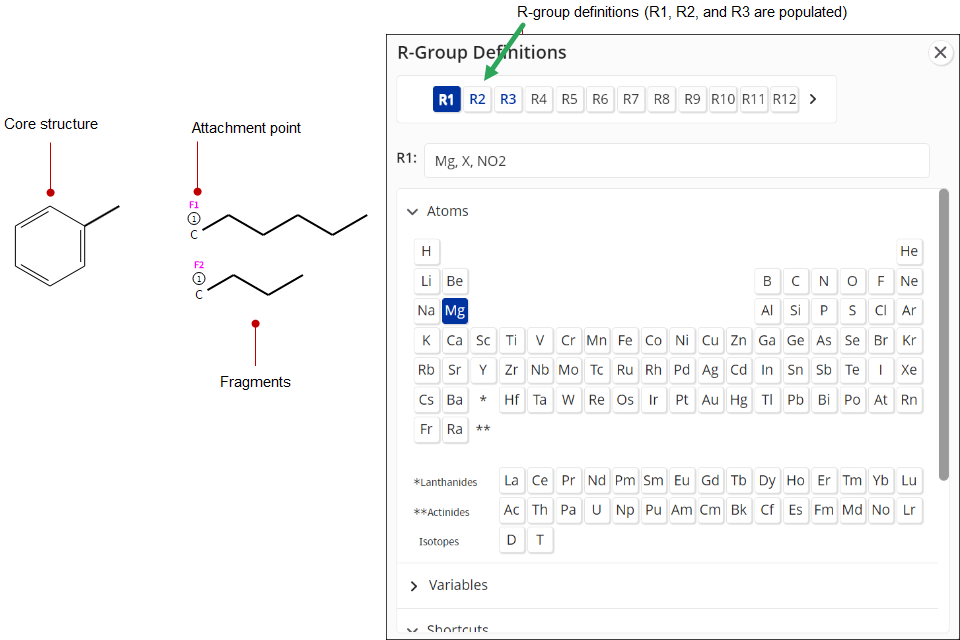
Click
the R-group  tool. The R-group
Definitions
dialog box appears.
tool. The R-group
Definitions
dialog box appears.
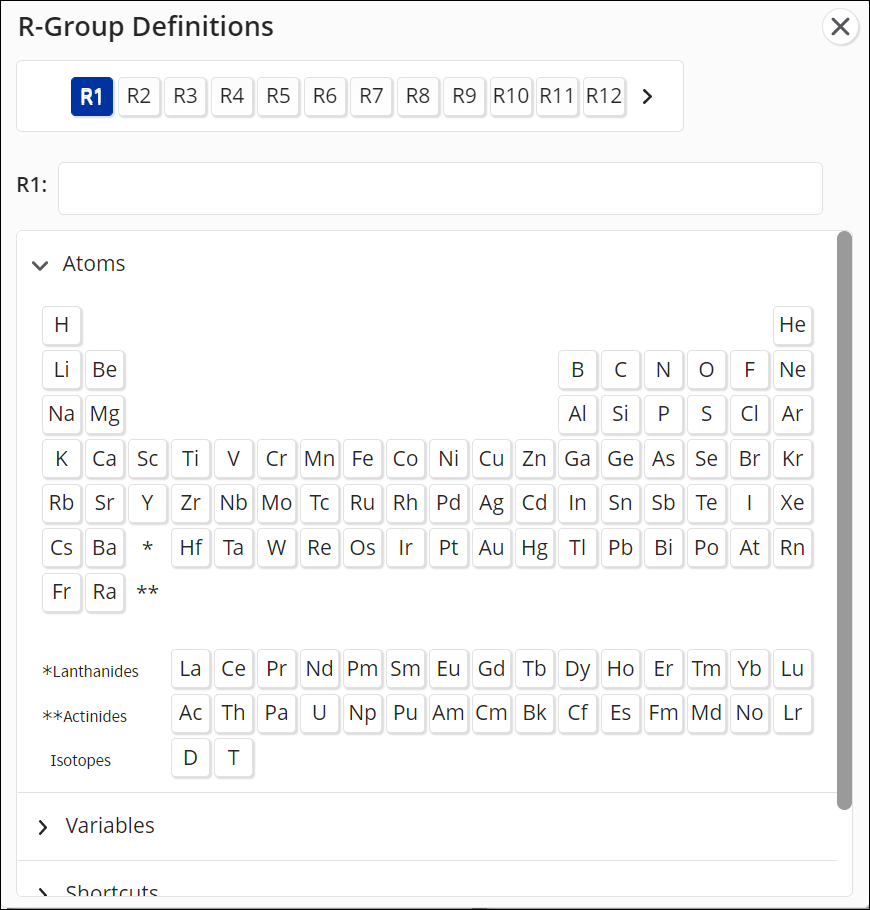
Define an R-group using the methods described below. Note: Non-fragment R-group definitions will match what is set in Preferences.
Select an R-group (e.g., R1).
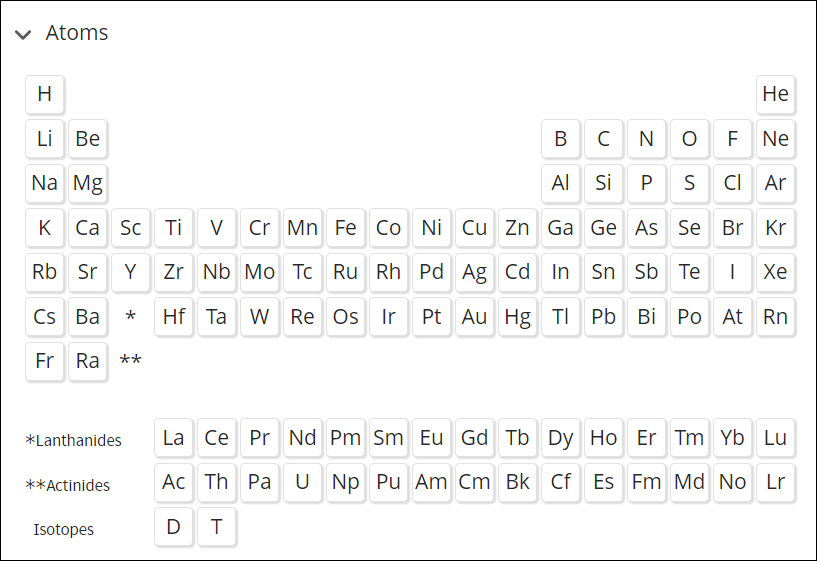
Select one or more atoms from the Atoms periodic table menu.
Select one or more variables from the Variables menu. (If necessary, click the arrow to open the Variables section.)
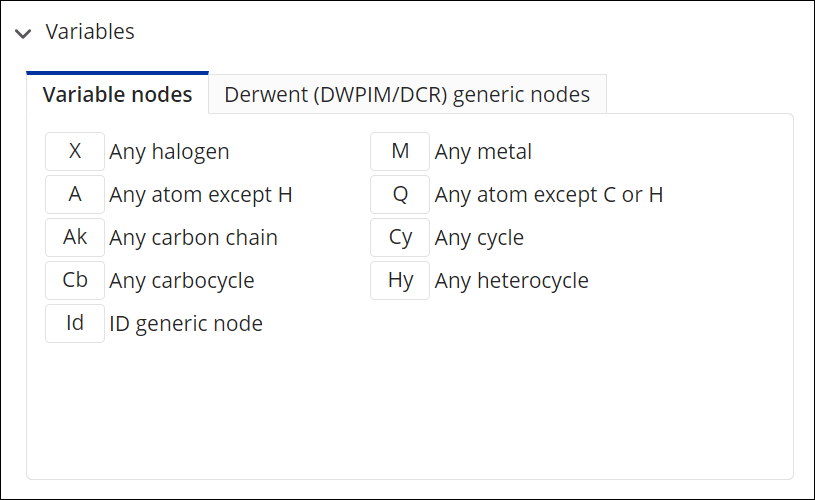
Select one or more structure shortcuts from the Shortcuts menu. (If necessary, click the arrow to open the Shortcuts section.)
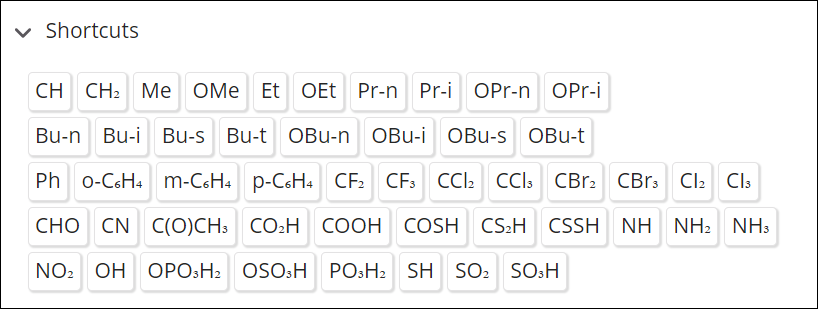
Select one or more structure fragments from the Fragments menu. (If necessary, click the arrow to open the Fragments section.)
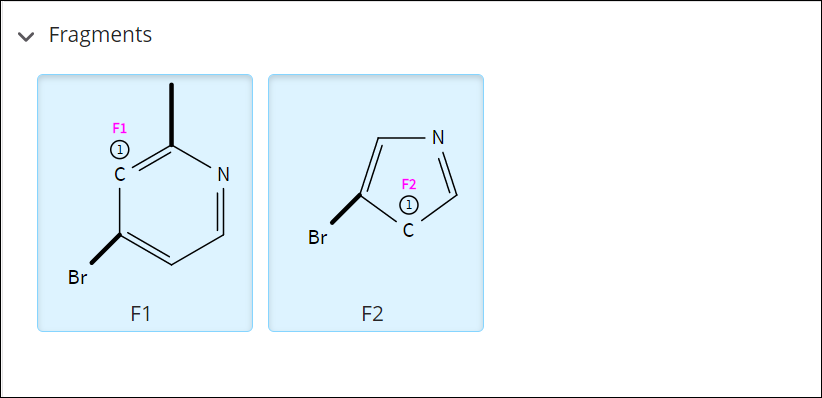
Fragments
are drawn in the Structure Editor window and attachment points are assigned using the Fn
 tool. A fragment cannot have more than
two attachment points.
tool. A fragment cannot have more than
two attachment points.
Or, type the symbols into the R-group field, separated by commas.
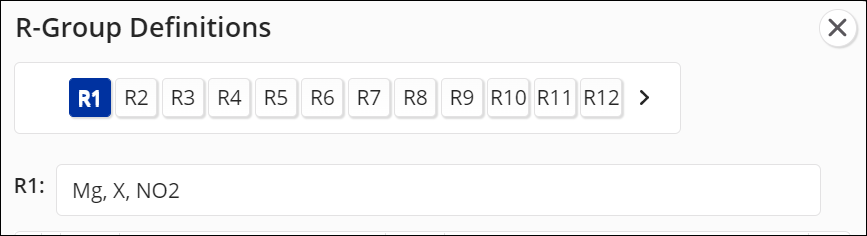
To assign an R-group to the query structure, click the R-group (e.g., R2) in the R-group Definitions dialog box, and then click the atom site on the core structure.
Repeat Step 3 until all the R-groups are assigned, and then click the X in the upper-right corner.
| Notes: |
|
Learn More
Drawing and Editing Structures